Would You Pick Emergency Medicine Again
A medical emergency is an acute injury or illness that poses an immediate adventure to a person's life or long-term health, sometimes referred to as a situation risking "life or limb". These emergencies may require assistance from another, qualified person, as some of these emergencies, such as cardiovascular (heart), respiratory, and gastrointestinal cannot be dealt with by the victim themselves.[1] Dependent on the severity of the emergency, and the quality of whatever treatment given, information technology may require the involvement of multiple levels of care, from first aiders through emergency medical technicians, paramedics, emergency physicians and anesthesiologists.
Any response to an emergency medical situation will depend strongly on the situation, the patient involved, and availability of resources to assistance them. It will as well vary depending on whether the Finn occurs whilst in hospital under medical care, or outside medical intendance (for example, in the street or alone at dwelling).
Response [edit]
Summoning emergency services [edit]
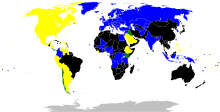
Implementation of the two ITU approved[2] emergency telephone numbers in the world:
112
9-one-1
112 and ix-1-ane
Other number or no redirection
For emergencies starting exterior medical intendance, a key component of providing proper care is to summon the emergency medical services (usually an ambulance), by calling for help using the appropriate local emergency telephone number, such equally 999, 911, 111, 112 or 000. After determining that the incident is a medical emergency (equally opposed to, for example, a police phone call), the emergency dispatchers will generally run through a questioning arrangement such every bit AMPDS in society to assess the priority level of the call, along with the caller'south name and location.
Outset aid and assisting emergency services [edit]
Those who are trained to perform first assist tin act inside the premises of the knowledge they take, whilst awaiting the next level of definitive intendance.
Those who are non able to perform get-go assistance can also help by remaining calm and staying with the injured or ill person. A mutual complaint of emergency service personnel is the propensity of people to oversupply around the scene of a victim, equally it is generally unhelpful, making the patient more than stressed, and obstructing the smooth working of the emergency services. If possible, first responders should designate a specific person to ensure that the emergency services are called. Another bystander should be sent to wait for their inflow and direct them to the proper location. Additional bystanders can be helpful in ensuring that crowds are moved abroad from the ill or injured patient, allowing the responder adequate infinite to piece of work.
Legal protections for responders [edit]
To preclude the filibuster of life-saving assistance from bystanders, many states of the The states accept "Expert Samaritan laws" which protect noncombatant responders who cull to assist in an emergency. In many situations, the general public may filibuster giving care due to fear of liability should they accidentally cause harm. Adept Samaritan laws often protect responders who act within the scope of their knowledge and grooming, as a "reasonable person" in the same situation would act.
The concept of implied consent can protect first responders in emergency situations. A get-go responder may not legally impact a patient without the patient's consent. Nevertheless, consent may be either expressed or implied:[three]
- If a patient is able to make decisions, they must requite expressed, informed consent earlier help is given.
- Notwithstanding, if a patient is too injured or ill to make decisions – for example, if they are unconscious, have an contradistinct mental status, or cannot communicate - unsaid consent applies. Implied consent means that handling can be given, considering it is assumed that the patient would want that care.
Usually, once care has begun, a start responder or start help provider may not leave the patient or stop intendance until a responder of equal or higher training (such as an emergency medical technician) assumes care. This tin can constitute abandonment of the patient and may discipline the responder to legal liability. Care must be continued until the patient is transferred to a higher level of care; the situation becomes too dangerous to go on; or the responder is physically unable to continue due to exhaustion or hazards.
Unless the state of affairs is specially hazardous and is likely to further endanger the patient, evacuating an injured victim requires special skills, and should exist left to the professionals of the emergency medical and fire service.
The chain of survival [edit]
The principles of the chain of survival employ to medical emergencies where the patient is non breathing and has no pulse. This involves 4 stages:
- Early access
- Early cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR)
- Early on defibrillation
- Early on advanced life support (ALS)
Clinical response [edit]
Inside hospital settings, an acceptable staff is mostly present to bargain with the boilerplate emergency situation. Emergency medicine physicians and anaesthesiologists have training to deal with near medical emergencies, and maintain CPR and Avant-garde Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) certifications. In disasters or complex emergencies, most hospitals have protocols to summon on-site and off-site staff rapidly.
Both emergency department and inpatient medical emergencies follow the basic protocol of Advanced Cardiac Life Support. Irrespective of the nature of the emergency, adequate blood pressure and oxygenation are required earlier the cause of the emergency tin can be eliminated. Possible exceptions include the clamping of arteries in severe hemorrhage.[ citation needed ]
Non-trauma emergencies [edit]
While the golden hour is a trauma treatment concept, two emergency medical weather have well-documented time-disquisitional handling considerations: stroke and myocardial infarction (heart attack). In the case of stroke, there is a window of three hours within which the benefit of thrombolytic drugs outweighs the risk of major bleeding. In the instance of a heart assault, rapid stabilization of fatal arrhythmias tin prevent sudden cardiac arrest. In add-on, there is a directly relationship between fourth dimension-to-treatment and the success of reperfusion (restoration of blood flow to the heart), including a fourth dimension-dependent reduction in the mortality and morbidity.[ citation needed ]
| | Wikibooks has a book on the topic of: First Aid |
See also [edit]
- List of medical emergencies
- Rescue squad
- Surgical emergency
References [edit]
- ^ AAOS tenth Edition Orange Book
- ^ "911 and 112 are the earth's standard emergency numbers, ITU decides". The Verge . Retrieved 2018-07-26 .
- ^ Caroline, Nancy (2013). Emergency Intendance in the Streets (Seventh ed.). Jones and Bartlett Learning. pp. 96–97.
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Medical_emergency
0 Response to "Would You Pick Emergency Medicine Again"
Postar um comentário